How to build a basic square wave bass sound in NI's Massive X synth
Use Massive X's oscillators to create a rave-style low end
Want all the hottest music and gear news, reviews, deals, features and more, direct to your inbox? Sign up here.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Native Instruments' Massive X is a fabulous instrument with real personality, and it can do things no other synth can. It's also good at the basics, though; here, we'll show you how to use its oscillators to craft a rave-esque bass sound.
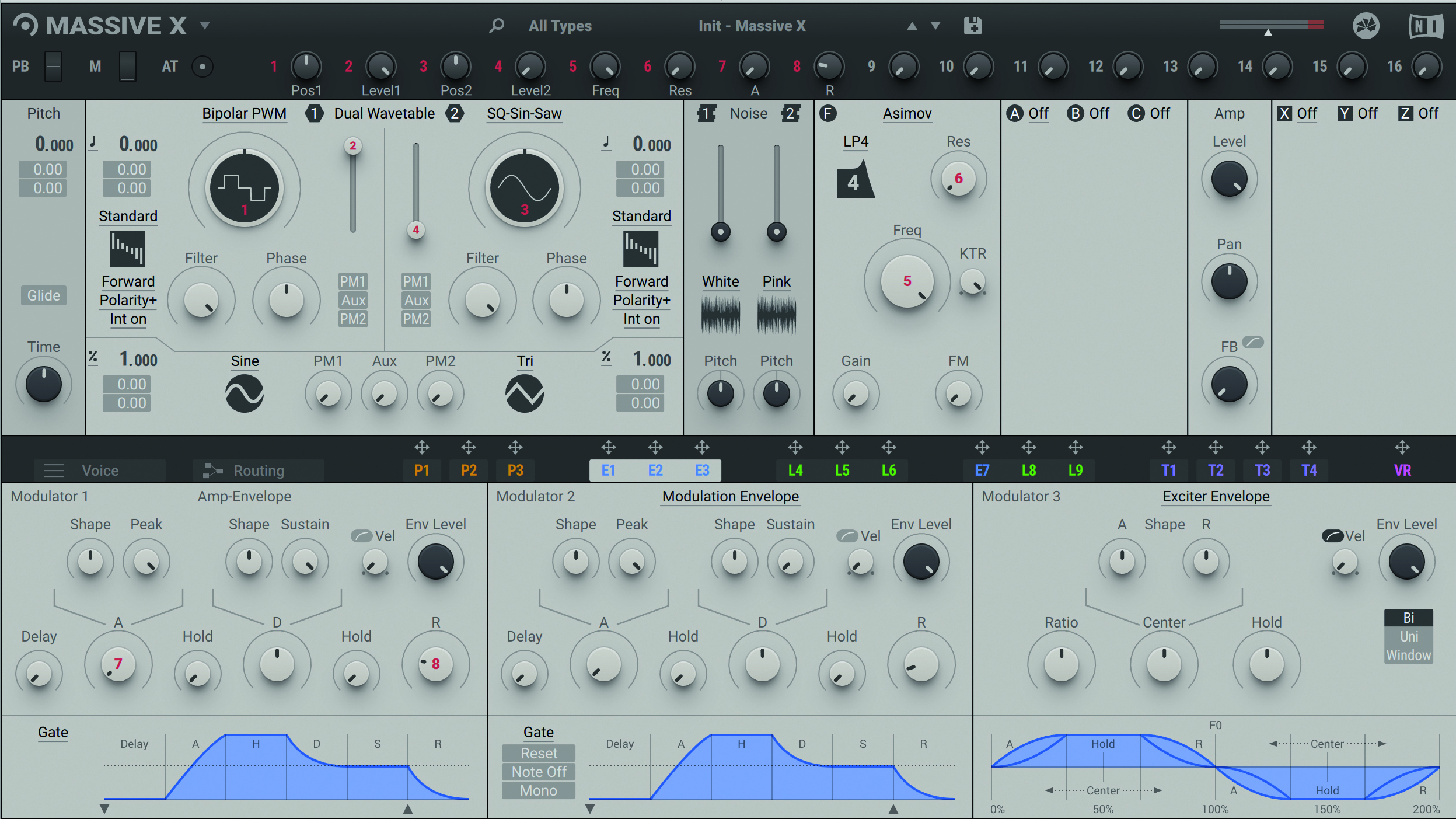
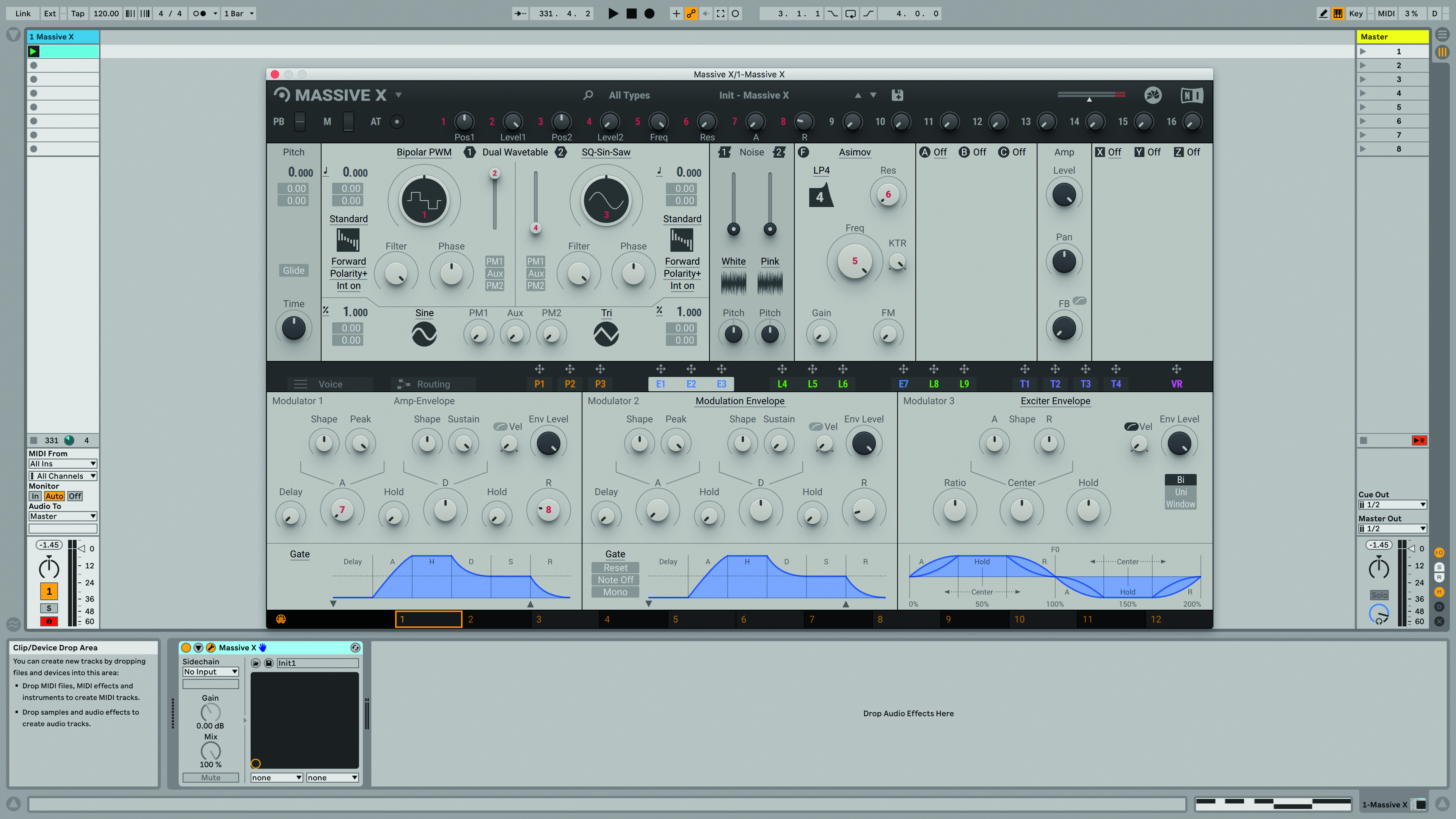
Step 1: Starting with the default Init - Massive X patch, call up the Basics >> Bipolar PWM wavetable in Osc 1. Massive X’s two main sound generators are wavetables – a wavetable oscillator is a collection of many single-cycle waves (referred to as ‘frames’).
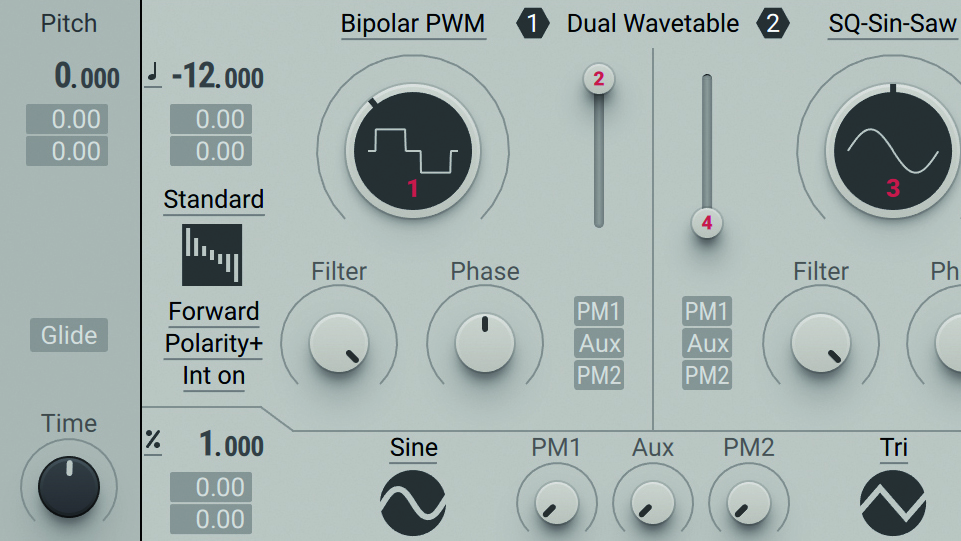
Step 2: Spin Osc 1’s main Wavetable Position knob to morph through the wavetable. This one is a collection of square waves at various pulse widths – scanning through these particular frames gives an effect like pulse width modulation. For a weightier tone, set Wavetable Position dial to 10-11 o’clock, then pitch the osc’s Tune down to -12 semitones.
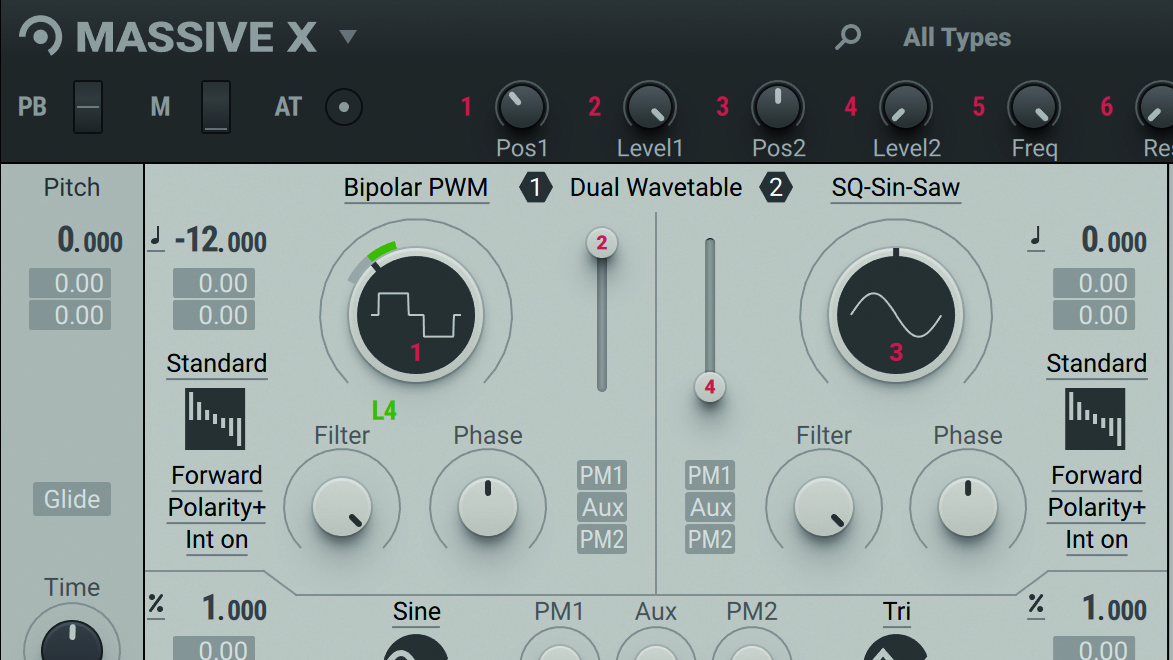
Step 3: To wiggle this faux ‘pulse width’ hands-free, click and drag LFO 4’s target cross, drop it into Osc 1’s Wavetable Position target slot, then drag up in the slot a little to dial in a small amount of bipolar modulation, shown by the green-coloured ‘Saturn’ ring around the knob.
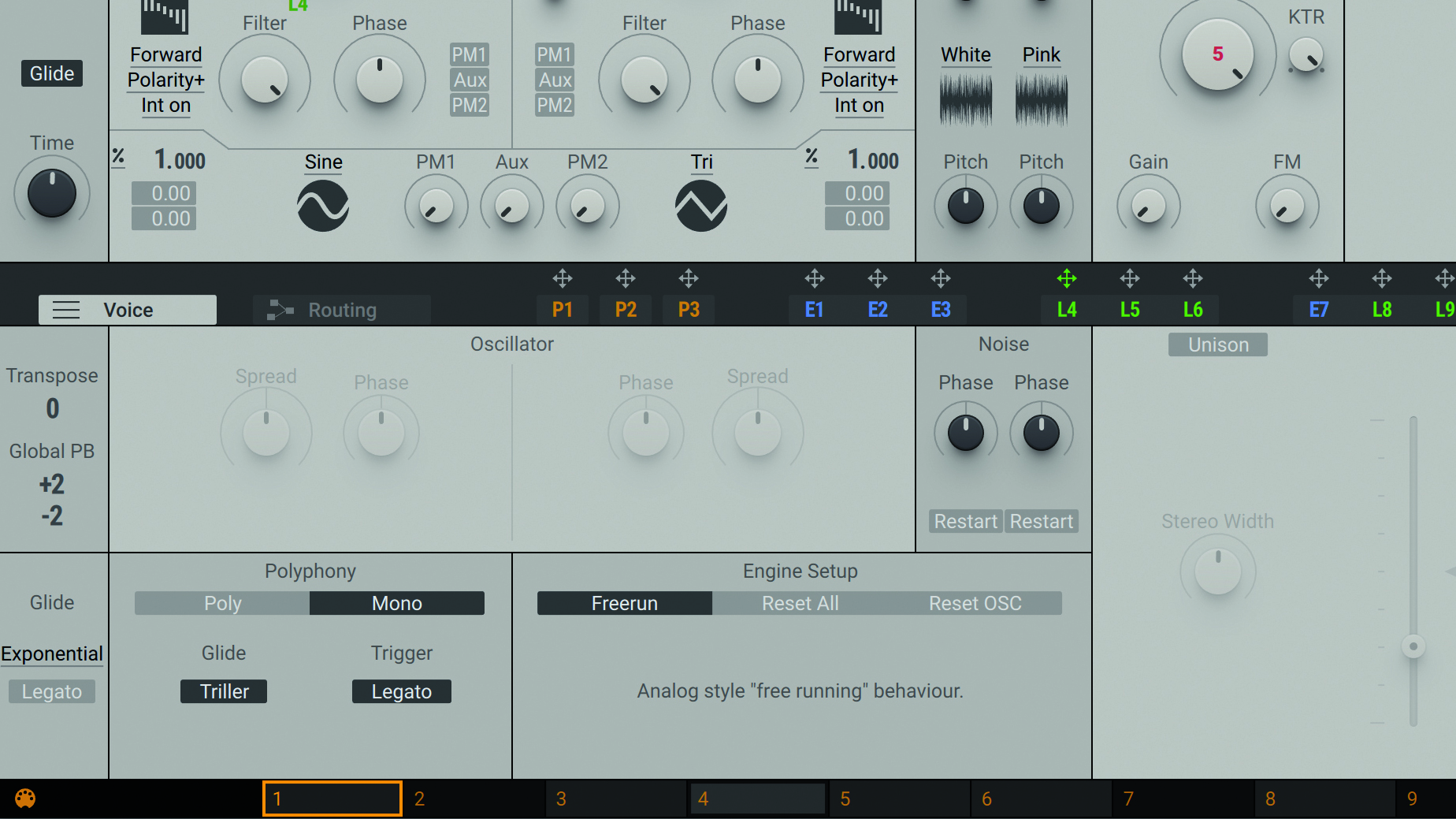
Step 4: Bass sounds are almost always monophonic, and we can set this up in Massive X’s Voice section. Pop open the Voice tab, then switch Polyphony from Poly to Mono. By deactivating the bottom-left Glide >> Legato button, then activating Glide (top left), the pitch of each played note will bend into the next, at a rate determined by the Glide knob.
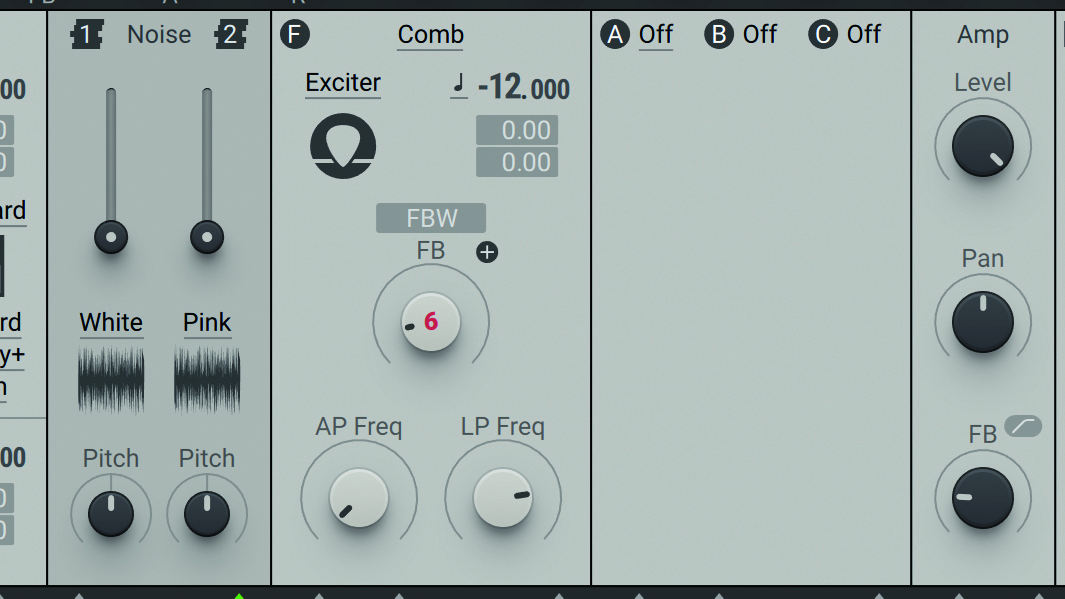
Step 5: We can beef up our straightforward square bass tone by getting Massive X’s Comb filter involved. Select the Comb filter type, tune it down to -12 semitones, then slightly raise the FB knob to introduce a tiny bit of tonal feedback. After that, raise the Amp >> FB knob to 9 o’clock for even more girth.
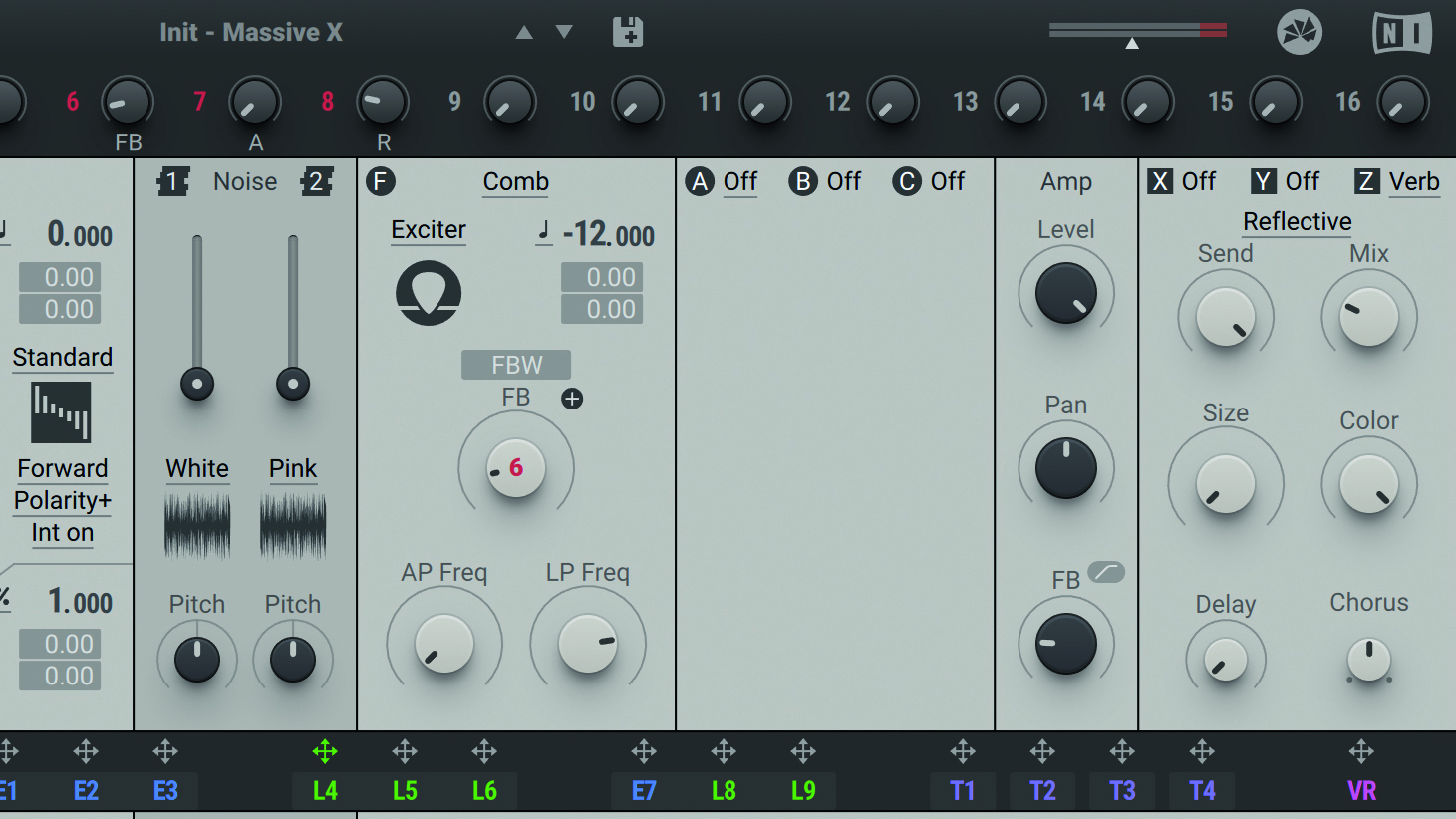
Step 6: Frequency-rich basses often benefit from some stereo widening in the midrange and treble areas, so in the synth’s final FX slot (Z), we call up the lush-sounding Reverb effect. Setting Size to fully anticlockwise and Colour to fully clockwise creates a tight, bright, widening effect that can be blended in to taste with the Mix knob.
Want all the hottest music and gear news, reviews, deals, features and more, direct to your inbox? Sign up here.
Computer Music magazine is the world’s best selling publication dedicated solely to making great music with your Mac or PC computer. Each issue it brings its lucky readers the best in cutting-edge tutorials, need-to-know, expert software reviews and even all the tools you actually need to make great music today, courtesy of our legendary CM Plugin Suite.
